In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what web design entails, how it differs from web development, and the tools, principles, and practices that shape modern websites.
1. What is Web Design?
Web design is the process of planning and creating the visual and functional elements of a website. This includes everything from layout and color schemes to fonts, graphics, and user interface (UI) elements.
Good web design ensures that a site is not only visually appealing but also user-friendly, accessible, and optimized for performance. It balances aesthetics with functionality, guiding users smoothly through their online experience.
2. Web Design vs. Web Development
Though often used interchangeably, web design and web development are distinct:
- Web Design focuses on the look and feel of a website.
- Web Development involves turning designs into functioning websites using coding languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Some tools (like Wix or Webflow) bridge the gap, allowing designers to create fully functional websites without needing to write code.
3. Essential Web Design Tools
Depending on your experience and goals, you might use:
Visual Design Tools
- Figma
- Adobe XD
- Sketch
- Photoshop
These allow for creating mockups and prototypes.
No-Code Website Builders
- Wix
- Webflow
- Squarespace
Ideal for beginners or quick deployment, these platforms offer drag-and-drop interfaces and responsive templates.
4. Principles of Good Web Design
Effective websites follow foundational design principles:
- Balance: Visual weight is distributed evenly.
- Contrast: Highlights important elements using differences in color, size, or shape.
- Emphasis: Directs focus to key elements like calls to action (CTAs).
- Hierarchy: Arranges content by importance.
- White Space: Enhances readability by avoiding clutter.
- Unity: Ensures all components feel cohesive and aligned.

These principles improve usability and enhance the visual appeal of your site.
5. Common Website Layouts
The layout is the foundation of your design. Popular types include:
- Single Column: Simple, mobile-friendly.
- F-Pattern: Mimics how users scan pages.
- Grid-Based: Organizes content into neat, modular sections.
- Asymmetrical: For creative or modern sites.
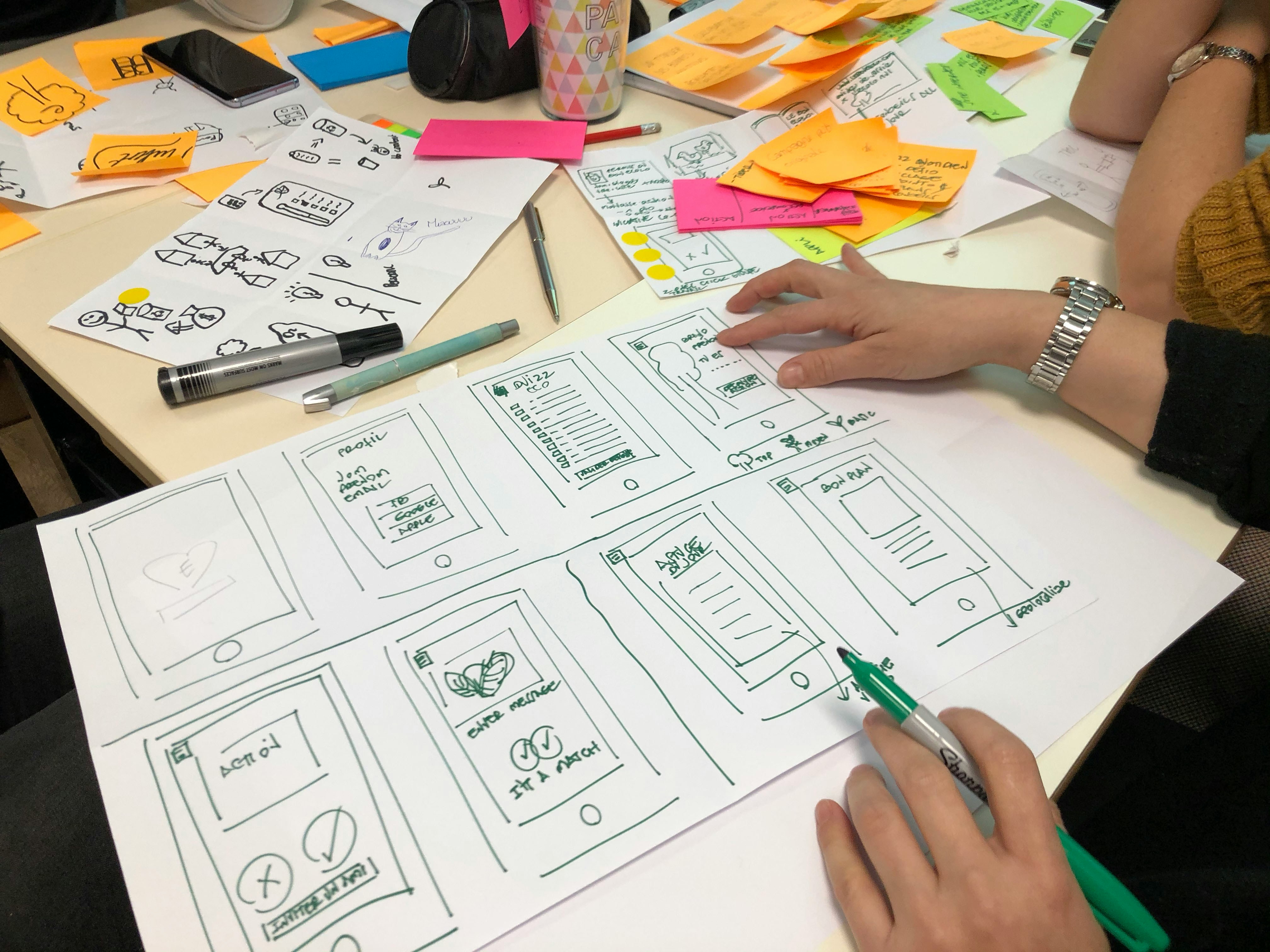
A well-chosen layout improves navigation and engagement.
6. Functional Elements of Web Design
Great design is also about performance and usability. Key components include:
- Navigation Menus: Clear and easy-to-use (e.g., top bar, hamburger menu).
- Responsive Design: Adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes.
- Page Speed: Fast-loading pages improve user experience and SEO.
- SEO Best Practices: Include metadata, alt text, and clean URLs.
- User Experience (UX): The site should be useful, usable, and enjoyable.

Accessibility is also critical—design with screen readers and keyboard navigation in mind.
7. Visual Elements of Web Design
Design is more than structure—visuals play a powerful role in engagement:
- Color Scheme: Reflects branding and mood.
- Typography: Enhances readability and conveys personality.
- Images & Videos: Add emotional and contextual depth.
- Animations: Provide visual feedback and guide interaction (used sparingly).
- Headers & Footers: Frame the page with navigation and important links.
A consistent visual language helps build trust and familiarity.
8. Conclusion
Web design is both an art and a science. It requires creative vision, technical know-how, and a user-first mindset. Whether you’re building a personal blog or an eCommerce store, understanding the fundamentals of web design will empower you to create engaging, effective websites.
Ready to design your own site? Start exploring, experimenting, and learning—your digital canvas awaits.
